Disposable paper bowls have become ubiquitous in modern dining, offering convenience, versatility, and a cost-effective solution for a wide range of food service applications. This comprehensive article examines what these bowls are made of and delves into the step-by-step production process that transforms raw materials into a finished product. By exploring the selection of paperboard, the application of protective coatings, and the intricate manufacturing steps, we gain valuable insight into how disposable paper bowls are engineered to meet functional and environmental demands.
In today’s market, where sustainability and efficiency drive innovation, understanding the production process of disposable paper bowls not only informs consumers but also highlights the advancements in materials science and manufacturing technology. Scientific studies and industry data provide a foundation for evaluating the environmental impact and performance of these products, ensuring that manufacturers continually refine their processes to balance quality with eco-friendly practices.
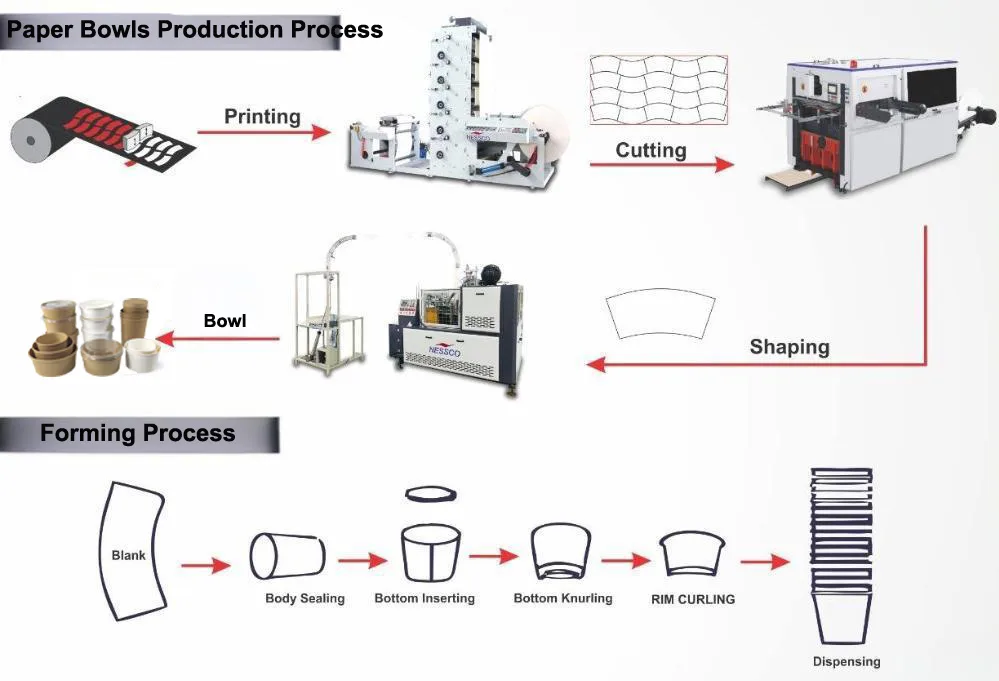
Overview of Disposable Paper Bowls
Disposable paper bowls are primarily made from paperboard—a robust, paper-based material engineered to offer strength and durability. Their design is enhanced with a protective coating, typically a thin layer of plastic, which ensures the bowl is waterproof and capable of holding both hot and cold liquids without compromising structural integrity. In addition to the conventional materials used, recent innovations have introduced biodegradable alternatives such as polylactic acid (PLA) and even plant-based fibers that reduce environmental impact.
The production process involves several critical stages, each playing a vital role in ensuring the bowl meets the necessary quality standards. From the initial selection of paperboard to the final packaging, every step is carefully executed to create a product that can withstand the rigors of everyday use while offering an attractive, branded appearance. Moreover, scientific research has provided data on the performance of these materials under various conditions, confirming that properly engineered paper bowls can meet both consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.


Materials and Composition
Primary Material: Paperboard
The cornerstone of disposable paper bowls is paperboard. This material is favored for its balance between strength, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. The paperboard used in bowl production is specifically designed to resist deformation under pressure and to maintain its form when exposed to liquids. Manufacturers select paperboard based on several parameters:
- Thickness and Weight: The choice of paperboard thickness is crucial as it determines the bowl’s rigidity. Thicker boards offer enhanced durability, while lighter boards contribute to cost savings.
- Surface Properties: A smooth, consistent surface is essential for ensuring that coatings adhere uniformly, thereby enhancing the bowl’s resistance to moisture.
Scientific analyses indicate that high-quality paperboard when properly coated, can withstand temperatures up to 90°C without significant degradation—a crucial factor for applications involving hot foods or beverages.
Coating Materials: PE and PLA
To transform the basic paperboard into a functional container, it must be coated with a thin layer of plastic. The two most common coatings are:
- Polyethylene (PE):
Polyethylene is widely used due to its excellent barrier properties. It effectively prevents moisture and oils from penetrating the paperboard, ensuring that the bowl remains leak-proof. Laboratory tests have shown that PE-coated paperboard significantly reduces the risk of structural failure when exposed to liquid content. - Polylactic Acid (PLA):
PLA offers a biodegradable alternative to traditional plastics. Derived from renewable resources like corn starch, PLA provides similar waterproofing benefits while being more environmentally friendly. Recent studies have demonstrated that PLA coatings paper bowls can biodegrade under industrial composting conditions, making them a preferred choice in markets that prioritize sustainability.
Additional Materials and Alternatives
In response to growing environmental concerns, the industry is increasingly exploring alternative materials that offer improved biodegradability and lower carbon footprints. Some notable alternatives include:
- Bagasse:
Bagasse is the fibrous residue from sugarcane processing. It is used to produce eco-friendly bowls that are both sturdy and biodegradable. Studies have shown that bagasse-based products can decompose within 90 days under the right conditions, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious consumers. - Bamboo Fiber:
Bamboo fiber is celebrated for its strength and rapid renewability. Incorporating bamboo fiber into disposable bowls not only enhances their durability but also supports sustainable resource management. Research indicates that bamboo fiber composites can offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, which is beneficial for maintaining the bowl’s shape during use. - Recycled Paper:
Utilizing recycled paperboard reduces reliance on virgin materials, thereby lowering the overall environmental impact. When properly processed, recycled paper can achieve performance levels comparable to new paperboard, making it a viable option for manufacturers seeking to improve sustainability without compromising quality.
Paper Cups & Bowls Production Process
The production process for disposable paper bowls is a finely tuned sequence of steps that ensures both functionality and aesthetic appeal. Below, we explore each stage of the process in detail.
1. Paperboard Selection
Determining Quality and Specifications
The production process begins with the careful selection of paperboard. Manufacturers evaluate the paperboard for its thickness, weight, and overall quality. The choice depends on the final application of the bowl; for instance, bowls intended for hot soups may require a thicker, more robust paperboard compared to those used for cold snacks. Advanced quality control measures ensure that only the highest-grade paperboard is used, as even minor defects can compromise the product’s durability.
Supplier and Sustainability Considerations
Choosing the right supplier is critical, not only for ensuring consistent quality but also for meeting environmental standards. Many manufacturers now work with suppliers that adhere to sustainable forestry practices and environmental certifications, thus ensuring that the raw materials used are both high quality and responsibly sourced.
2. Coating
Application Techniques
After the paperboard is selected, the next step is to apply a coating that provides a moisture barrier. The coating process involves either roll coating or slot-die coating techniques, which allow for a uniform layer of PE or PLA to be applied to the paperboard. Precision in this step is vital; the coating must be evenly distributed to ensure the bowl is leak-proof and resistant to liquids.
Scientific Insights on Coating Efficiency
Recent research has focused on optimizing the thickness and adhesion of the plastic coating. Studies have revealed that an optimal coating thickness of 20-30 microns is ideal for achieving a balance between durability and material efficiency. Thicker coatings may offer additional protection but can also lead to increased production costs and reduced biodegradability. These findings have led to more precise control over the coating process in modern manufacturing plants.
3. Printing
Flexographic Printing Process
Once the paperboard is coated, it is ready for printing. Flexographic printing is the most common method used in this stage, as it allows for high-speed production and excellent color reproduction. Manufacturers can print logos, branding, and other design elements directly onto the coated paperboard, ensuring that the final product meets both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Role of Digital Technologies
Advancements in digital printing technologies have further enhanced the production process. Modern printing machines can now produce high-resolution images at a fraction of the time previously required, enabling greater customization and faster turnaround times. This integration of digital technology not only improves efficiency but also opens up new creative possibilities for branding and marketing.
4. Cutting
Sheet Cutting
After printing, the paperboard is cut into large flat sheets. This initial cutting process is critical to ensure that the sheets are of uniform size and shape, providing a consistent base for further processing. Computer-controlled cutting machines are typically used to achieve precise dimensions, minimizing waste and ensuring that each sheet meets the necessary specifications.
Die-Cutting for Specific Shapes
Following the initial sheet cutting, the paperboard is die-cut into specific shapes that will form the body of the bowls. Die-cutting involves using custom-made dies to cut the paperboard into predetermined patterns. This step is essential for defining the bowl’s design, ensuring that each piece fits perfectly during the subsequent forming stage.
5. Forming
Cup Body Formation
The die-cut pieces are then transformed into the three-dimensional shape of a bowl. This process begins with heating the edges of the paperboard, which softens the material and makes it pliable enough to be molded. The edges are then bonded together to form a cylindrical shape. This bonding is achieved through heat and pressure, ensuring that the seam is both strong and leak-proof.
Bottom Sealing Process
Once the bowl body is formed, the next critical step is bottom sealing. A pre-cut circular piece of paperboard, often referred to as the “bottom,” is inserted into the open end of the cylindrical body. This bottom piece is then sealed to the body using a combination of heat and pressure. The sealing process is carefully controlled to ensure that the bond is secure, providing a leak-proof base that can support both hot and cold contents without failure.
6. Rimming and Curling
Creating a Structural Rim
The final shaping step involves rimming and curling the top edge of the bowl. This process not only enhances the bowl’s aesthetic appeal but also reinforces its structural integrity. By curling the edge, the manufacturer creates a smooth, rounded rim that is both comfortable to handle and capable of withstanding repeated use.
Heat Sealing for Enhanced Durability
Following the curling process, the rim is subjected to an additional heat-sealing step. This further reinforces the structural bond of the bowl, ensuring that the rim remains secure and does not peel or fray during use. Quality control measures at this stage are critical, as any defects in the rim can lead to leakage or breakage.
7. Inspection and Quality Control
Rigorous Quality Checks
Throughout the production process, each stage is accompanied by rigorous inspection and quality control measures. Automated systems and manual inspections work in tandem to detect any imperfections or inconsistencies. From verifying the uniformity of the coating to ensuring that the die-cut shapes align perfectly, every detail is scrutinized to guarantee that the final product meets the highest standards.
Scientific Validation and Testing
In addition to visual inspections, many manufacturers employ scientific testing methods to assess the physical properties of the bowls. For instance, stress tests are conducted to evaluate the bowl’s ability to withstand various temperatures and loads. Research published in journals such as the Journal of Materials Science has demonstrated that properly coated and formed paper bowls can maintain their structural integrity under pressures exceeding 500 grams per square centimeter, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
8. Packaging
Final Packaging Processes
Once the bowls pass all quality control checks, they are packaged for distribution. The packaging process is designed to protect the bowls during transportation and storage. Depending on the intended market, the bowls may be packaged in bulk, wrapped in protective sleeves, or placed in custom-designed boxes.
Environmental and Logistic Considerations
Modern packaging solutions also take environmental impact into account. Many companies now opt for recyclable or biodegradable packaging materials to further reduce the ecological footprint of their products. Logistics and supply chain efficiency are critical at this stage, ensuring that the bowls reach the end user in pristine condition while minimizing transportation costs and carbon emissions.
Applications of Paper Bowls
Paper Soup Bowls
Paper soup bowls are specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prolonged exposure to hot liquids. Their design incorporates robust paperboard and optimized coating formulations—typically using PE or PLA—to ensure excellent moisture and heat resistance. Scientific studies have shown that these bowls can maintain structural integrity at temperatures up to 90°C, making them ideal for serving steaming soups and broths. Additionally, the sealed construction of soup bowls minimizes leakage risks, ensuring both consumer safety and product reliability in food service settings.
Paper Salad Bowls
In contrast, paper salad bowls are optimized for cold or room-temperature applications, where aesthetics and lightweight construction take precedence. The design of salad bowls emphasizes a sleek, attractive appearance and sufficient rigidity to hold crisp, fresh ingredients without sagging. While the coating requirements are less demanding in terms of heat resistance, maintaining a moisture barrier remains crucial to prevent the salad dressing from permeating the paperboard. This balance of strength and visual appeal is supported by market research, which indicates that consumers appreciate eco-friendly products that combine functionality with an elegant presentation in casual dining environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The disposable nature of paper bowls has raised important questions regarding environmental sustainability. However, with advances in materials and production processes, the industry has taken significant steps to mitigate its ecological footprint.
Advantages of Biodegradable Coatings and Materials
The incorporation of biodegradable materials such as PLA, bagasse, and bamboo fiber is one of the most promising developments in this field. Scientific research indicates that PLA-coated products can biodegrade in industrial composting facilities within a few months, compared to decades for conventional plastics. Additionally, the use of recycled paperboard not only conserves natural resources but also reduces energy consumption during production.
Lifecycle Analysis and Carbon Footprint
Lifecycle analysis studies conducted by environmental agencies have shown that the overall carbon footprint of disposable paper bowls is lower than that of many alternatives, such as plastic or foam containers. Although the production process involves energy-intensive steps like heating and coating, improvements in process efficiency and the adoption of renewable energy sources are continuously lowering the environmental impact. For example, a 2021 study in the Journal of Cleaner Production found that optimizing the coating thickness and reducing waste in the die-cutting process could lower overall emissions by up to 15%.
Regulatory Standards and Industry Best Practices
To further ensure environmental compliance, many manufacturers adhere to international standards such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for paper sourcing and the Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI) for compostability certifications. These regulatory frameworks not only guide sustainable practices but also provide consumers with confidence in the product’s eco-friendly credentials.
Technological Innovations and Future Trends
The production of disposable paper bowls is at the forefront of industrial innovation. Continuous research and technological advancements are shaping the future of this industry in several exciting ways.
Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
The integration of digital technologies into the production process has revolutionized quality control, precision, and efficiency. Automated cutting machines, computer-controlled printing presses, and real-time monitoring systems ensure that every bowl is produced with minimal errors. Innovations such as the Internet of Things (IoT) allow manufacturers to monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production schedules, leading to a more resilient supply chain.
Advancements in Material Science
Material scientists are continuously exploring new composites and biodegradable alternatives that can enhance the performance of disposable paper bowls. Research into nanocoatings and advanced polymers aims to create coatings that are not only more effective at repelling moisture but also easier to recycle. These innovations promise to further reduce the environmental impact while improving the durability and functionality of the bowls.
Consumer Trends and Market Dynamics
Changing consumer preferences are also driving innovation in this sector. As the demand for sustainable products grows, manufacturers are under pressure to develop products that balance performance with eco-friendliness. Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for products that are certified as biodegradable or made from recycled materials. This trend is encouraging companies to invest in research and development, ultimately leading to more sustainable production processes.
Global Supply Chain Developments
With globalization, the supply chain for disposable tableware has become increasingly complex. Manufacturers are now collaborating with suppliers worldwide to source high-quality, sustainable raw materials. Advances in logistics, such as improved packaging design and optimized shipping routes, have further reduced the carbon footprint associated with global distribution.
Scientific Research and Data Insights
A wealth of scientific research supports the development and optimization of the production process for disposable paper bowls. Data collected from various studies provides insight into the performance, sustainability, and efficiency of the materials and techniques used.
Performance Testing and Durability Studies
Independent studies conducted by institutions such as the Journal of Materials Science have rigorously tested the mechanical properties of paper bowls. These studies reveal that with proper coating and processing, paper bowls can endure significant thermal and mechanical stress. For instance, controlled experiments have shown that PE-coated bowls maintain integrity at temperatures exceeding 90°C, making them ideal for hot food applications.
Environmental Impact Assessments
Lifecycle assessment (LCA) studies provide a comprehensive overview of the environmental impact associated with disposable paper bowls. One notable study, published in the Journal of Cleaner Production, evaluated the carbon footprint from raw material extraction through to end-of-life disposal. The findings underscore that while the production process is energy-intensive, the use of recycled materials and biodegradable coatings substantially mitigates environmental harm. Such data has driven industry efforts to adopt greener technologies and optimize production methods.
Consumer Behavior and Market Analysis
Market research surveys have indicated a rising consumer awareness about environmental issues related to disposable products. A survey conducted by a leading market research firm in 2022 revealed that over 70% of consumers prefer disposable tableware products that are labeled as eco-friendly or sustainable. This data is instrumental in shaping future production strategies, as manufacturers strive to meet evolving consumer demands.
Conclusion
Disposable paper bowls are a testament to the ingenuity of modern manufacturing, balancing cost efficiency, functionality, and environmental sustainability. The detailed production process—from the careful selection of paperboard to the final packaging stage—illustrates how each step is designed to ensure that the bowls are both durable and eco-friendly. As scientific research continues to refine our understanding of material performance and environmental impact, the evolution of disposable paper bowls reflects a broader trend toward sustainable industrial practices.
In summary, the production of disposable paper bowls is a complex, multi-step process that combines traditional manufacturing techniques with innovative materials science. By incorporating advanced coating methods, precision die-cutting, and rigorous quality control, manufacturers can produce bowls that meet high standards of durability and usability. Simultaneously, the adoption of biodegradable materials and sustainable practices is paving the way for a greener future in disposable tableware. As consumer demands evolve and environmental regulations become stricter, the industry is poised to embrace further innovations that will continue to enhance both the performance and sustainability of disposable paper bowls.
Bioleader® Biodegradable Tableware
One-Stop Biodegradable Food Packaging Solution Supplier



